Anatomy of the penis
4
The tissue within the corpora cavernosa and the corpus
spongiosum is formed by a network of smooth muscle
(trabeculae) which delimits the vascular spaces (gaps
cavernous).
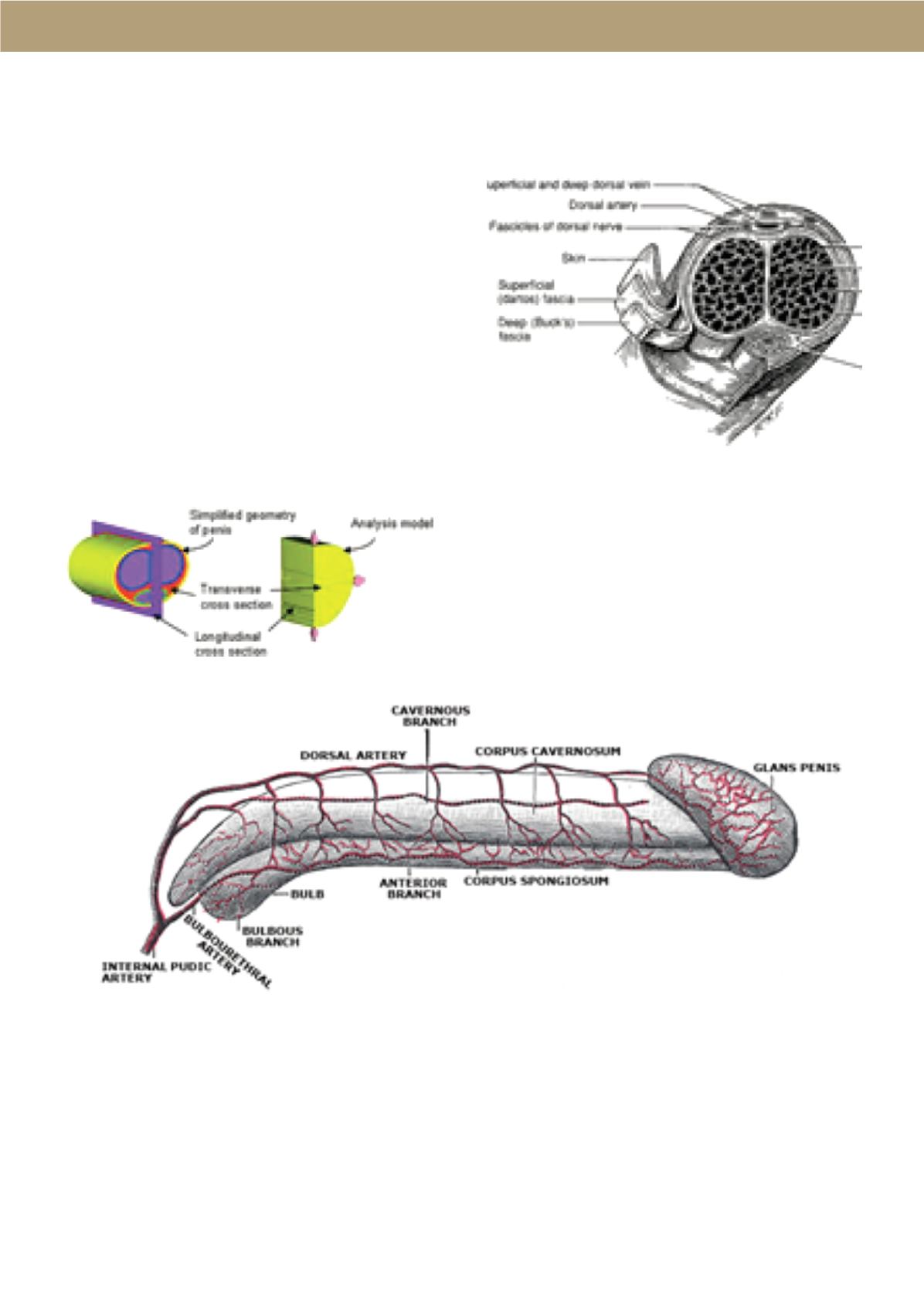
The body of the penis is composed of two cylinders
called corpora cavernosa which are placed on the dorsal
and lateral surface of the organ. Below it is placed the
corpus spongiosum, which contains the urethra, that is
the channel through which urine and semen are carried
outside. At the end of the corpora cavernosa this
channel widens and forms a conical structure called
glans. The corpora cavernosa are covered by a thick
fibrous sheath, the tunica albuginea, which, at the point
where the cavernous bodies join, forms a perforated
septum which allows these structures to function as a
single unit.