Treatment
4
The treatment of this pathology is only surgical and can
be performed at any time in adults.
The aim of surgery is to correct curvature and allow
satisfactory intercourse.
The major type of repair for congenital penile curvature
may be considered as shortening procedures.
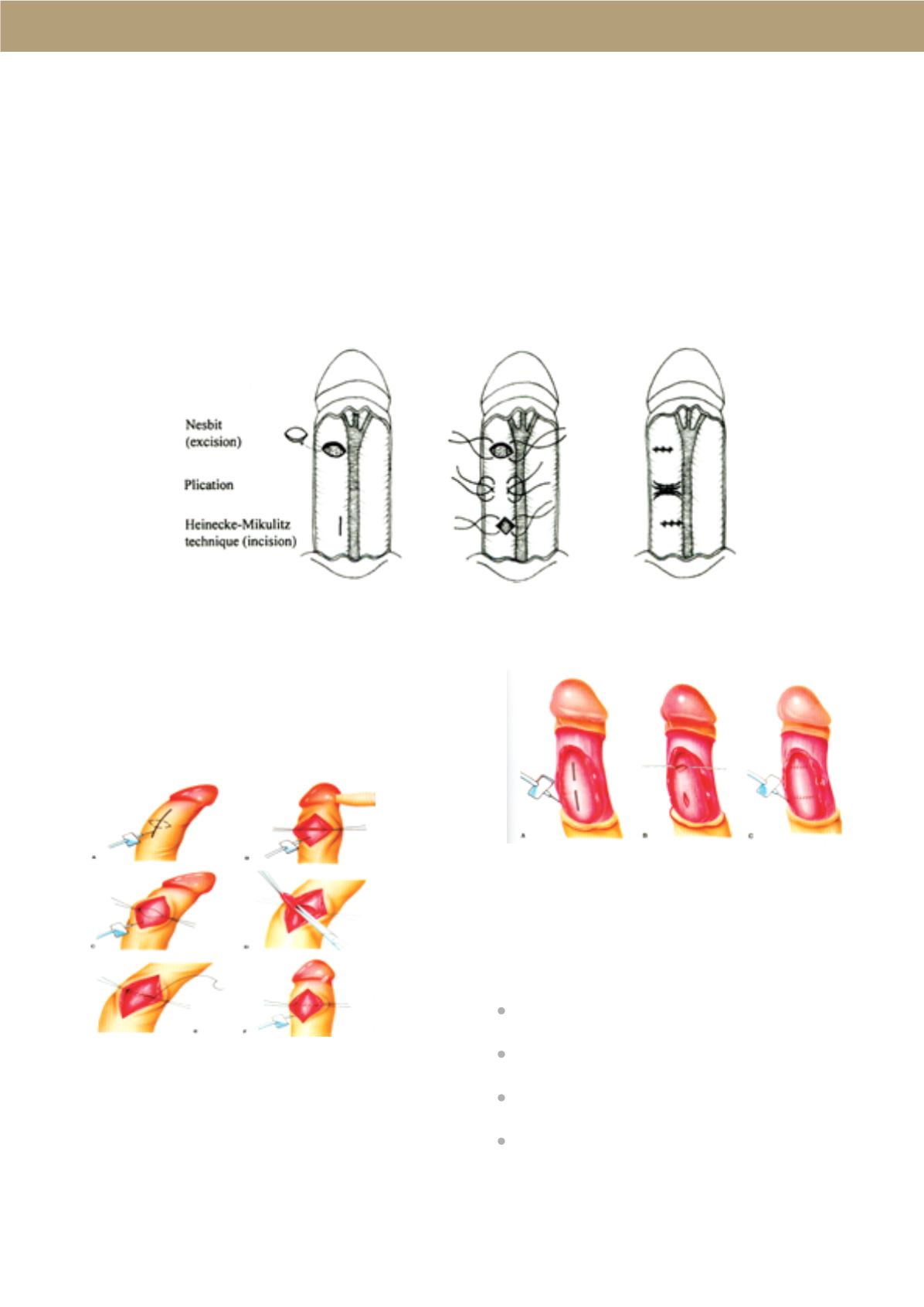
Penile shortening procedures include the Nesbit wedge
resection and the Plication techniques. All these
procedures are performed on the convex side of the
penis and are used almost exclusively with high
curvature correction rates.
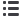
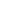
The Nesbit operation is based on a 5 to 10 mm
transverse elliptical excision of the tunica albuginea or
approximately 1 mm for each 10° of curvature. This
excision is performed on the convex side of the penis
and closed in a horizontal way.
Nesbit operation
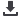
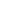
Plication procedures use the same principle as the
Nesbit operation but are simpler to perform. They are
based on single (or multiple) longitudinal incisions
closed in a horizontal way or on single (or multiple)
plication knots without tunica albuginea incision.
All these techniques are performed on the convex side
of the penis.
single (or multiple) longitudinal incisions closed in a
horizontal way
The overall short - and long-term results of the Nesbit
operation and the other Plication techniques are
excellent:
Complete penile straightening is achieved in 67 to
97% of patients.
Recurrence of the curvature is uncommon (about
10%)
Risk of postoperative erectile dysfunction and penile
hypoesthesia is minimal (less than 6%)
Penile shortening is the most commonly reported
outcome. However, shortening of only 1–1.5 cm has
been reported for about 85% of patients, patients
often perceive the loss of length as greater than it
actually is. Which is rarely the cause for postoperative