What causes Peyronie’s disease?
4
Medical experts do not know the exact cause of
Peyronie’s disease. Many believe that Peyronie’s disease
may be the result of
acute injury to the penis
chronic, or repeated, injury to the penis
autoimmune disease—a disorder in which the body’s
immune system attacks the body’s own cells and
organs with low levels of the male hormone
testosterone.
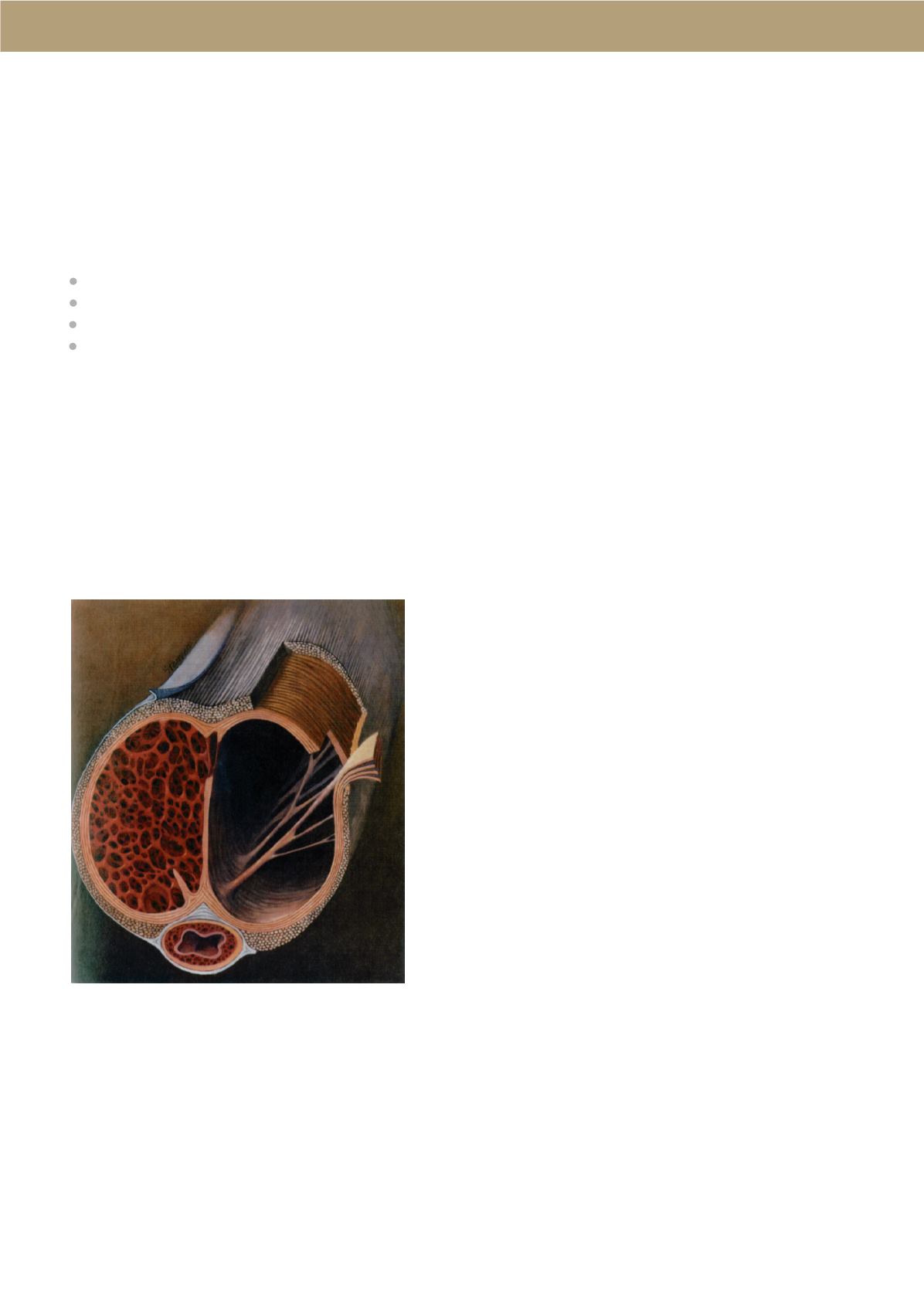
Injury to the Penis
Medical experts believe that hitting or bending the penis
may injure the tissues inside. A man may injure his
penis during sex, athletic activity, or an accident. Injury
ruptures blood vessels, which leads to bleeding and
swelling inside the layers of the tunica albuginea.
Swelling inside the penis will block blood flow through
the layers of tissue inside the penis. When the blood
can’t flow normally, clots can form and trap immune
system cells. As the injury heals, the immune system
cells may release substances that lead to the formation
of too much scar tissue. The scar tissue builds up and
forms a plaque inside the penis. The plaque reduces the
elasticity of tissues and flexibility of the penis during
erection, leading to curvature. The plaque may further
harden because of calcification––the process in which
calcium builds up in body tissue.
Autoimmune Disease
Some medical experts believe that Peyronie’s disease
may be part of an autoimmune disease. Normally, the
immune system is the body’s way of protecting itself
from infection by identifying and destroying bacteria,
viruses, and other potentially harmful foreign
substances. Men who have autoimmune diseases may
develop Peyronie’s disease when the immune system
attacks cells in the penis. This can lead to inflammation
in the penis and can cause scarring.